
Blockchain Consensus Algorithms: How Market Makers and Liquidity Providers Benefit
In the ever-evolving realm of cryptocurrency, the success of market makers and liquidity providers depends not just on market trends and trading insights, but also on a deeper understanding of the underlying technology: blockchain. At the heart of this technology lies a crucial, yet often overlooked component — the consensus algorithm. This is more than a mere technicality; it's the engine that drives the entire system, influencing everything from transaction speed to the very security of the assets you trade.
But how exactly do concepts like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake translate into real-world gains or losses for you? How can a nuanced understanding of these mechanisms empower you to make more informed, strategic decisions? In this exploration, we'll dive into the intricacies of consensus algorithms, shedding light on their direct impact on your trading strategies. Our aim is to demystify the technical jargon and provide you with tangible insights, enabling you to not just navigate but thrive in the complex world of crypto trading.
What are Blockchain Consensus Algorithms? Cutting Through the Jargon to the Core Principles.
Consensus algorithms are processes used to achieve agreement on a single data value among distributed processes or systems, ensuring coordination, consistency, reliability, and security in blockchain networks. They play a crucial role in defining who validates and creates the next block in the blockchain, thereby avoiding disputes among conflicting variations of a blockchain while ensuring decentralization.
Impact of Different Consensus Types on Transaction Throughput and Costs
Transaction throughput refers to how many transactions a blockchain can process in a given time frame, like transactions per second (TPS). Costs relate to the fees associated with processing these transactions. Different consensus mechanisms can significantly affect both these aspects.
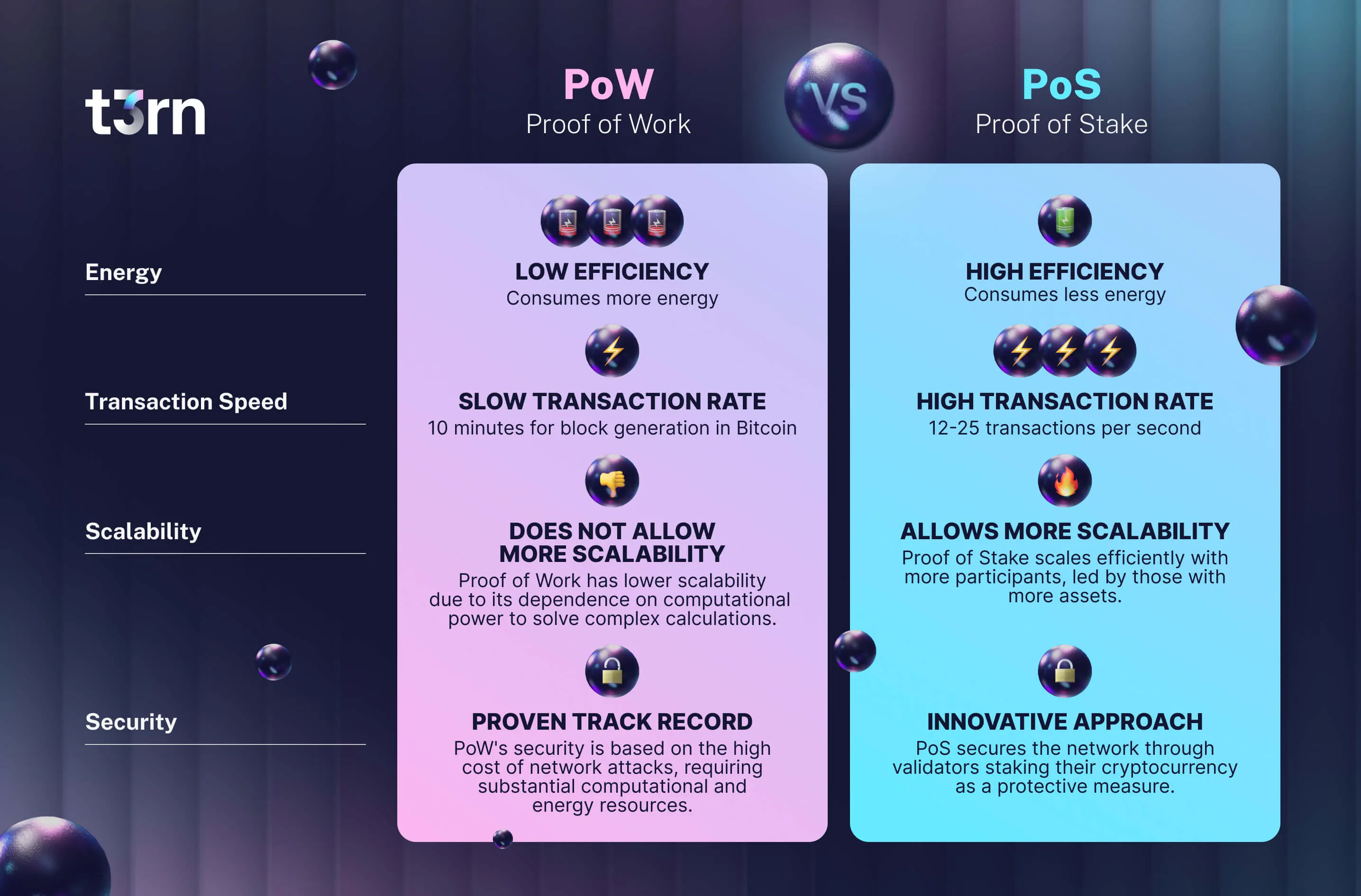
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work (PoW) is a decentralized consensus mechanism that requires network members to expend effort in solving an encrypted hexadecimal number. PoW makes double-spending incredibly difficult because changing any part of the blockchain would involve re-mining all subsequent blocks. However, PoW is a slower validation method than other mechanisms and requires vast amounts of energy, which only increases as more miners join the network.
In simpler terms, Proof of Work requires participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical problems, which in turn validates transactions and secures the network.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake, on the other hand, involves participants, known as validators, who are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to 'stake' as collateral, making it more energy-efficient than PoW. Staking ETH means locking up a certain amount of your Ethereum coins as a form of security deposit to participate as a validator in the network.
PoS is designed to reduce network congestion and address environmental sustainability concerns surrounding the PoW protocol.
PoS offers greater transaction throughput and increased scalability compared to PoW. Ethereum's existing network can handle roughly 30 transactions each second compared to Bitcoin with around 5 TPS.
Market Making Algorithms: Real-time Impacts on Trading and Liquidity
Market making algorithms, integral to providing liquidity in financial markets, are also influenced by these consensus mechanisms. For instance, the spread-based strategy, where securities are bought at bid prices and sold at ask prices, can be more effectively executed in a PoS environment due to higher transaction throughput and lower costs. High-frequency trading (HFT), another common strategy in market making, can benefit from the increased speed and scalability of PoS systems.
Case Study: Ethereum's Shift from PoW to PoS
Ethereum's transition from PoW to PoS, known as 'The Ethereum Merge', marked a significant shift in the cryptocurrency sector. This transition transformed the role of Ethereum (ETH), which was previously used to reward crypto miners, into a stake that safeguards the integrity of the blockchain. Validators risk losing their stake in a process known as slashing, this is a penalty mechanism in Proof of Stake systems. It's like a fine for validators who break network rules or operate in a malicious manner. This could involve losing a portion of their staked coins, ensuring that validators act in the network's best interest.
The shift to PoS was driven by Ethereum's commitment to sustainability and reducing its carbon footprint. This objective was successfully achieved, with Ethereum's annualized energy consumption dropping to approximately 7.5 TWh, consuming 15 times less energy than Bitcoin. The transition to PoS also democratized network participation by requiring lower resource requirements for validator nodes and removed technical barriers to scalability.
Implications for market making or liquidity provision after “The Merge”
To become a market maker or liquidity provider in this new environment, you would need to understand the dynamics of the PoS system and adapt your strategies accordingly.
Here are some steps you could take:
- Stake ETH: To participate in the PoS system, you would need to stake ETH. The minimum amount required to become a validator is 32 ETH. Staking not only allows you to participate in the validation process but also earns you rewards in the form of new ETH.
- Understand the Risks: Staking comes with its own set of risks. For instance, if a validator behaves dishonestly or fails to validate correctly, they risk slashing. Therefore, it's crucial to ensure that your validation node is set up correctly and operates reliably. A validation node is essentially a computer on the blockchain network that participates in the validation process. It checks and confirms the legitimacy of new transactions and blocks according to the consensus rules.
- Leverage Liquid Staking Services: If the requirement of 32 ETH is too high or the process of setting up a validation node is too complex, you could consider using liquid staking services. These services allow you to stake a smaller amount of ETH and still participate in the validation process.
Conclusion: Navigating the Blockchain with Informed Strategies
As we've explored, the world of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency is not just about the fluctuations of market prices. The underlying mechanics, particularly the consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), play a fundamental role in shaping the landscape. From impacting transaction speeds and costs to influencing environmental sustainability, these algorithms are at the core of how blockchain networks operate and evolve.
The shift from PoW to PoS, exemplified by Ethereum's transition, is not merely a technical update. It represents a paradigm shift in how we engage with cryptocurrencies. For market makers and liquidity providers, understanding these changes is not optional; it's essential for adapting strategies, managing risks, and seizing opportunities in a rapidly changing environment.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, staying informed and agile will be crucial. Whether you're a seasoned trader, a curious investor, or a technology enthusiast, the knowledge of how these systems work under the hood empowers you to make smarter decisions. By embracing this understanding, you position yourself not just as a participant in the blockchain space, but as a forward-thinking innovator ready to navigate the future waves of technological advancement.
In the world of blockchain and crypto trading, knowledge isn't just power—it's profit.
Join Multichain Matters
Gain a competitive edge on interoperability and stay up to date with the development of t3rn. Get insights from Maciej Baj (Founder & CTO), alongside 15,000 subscribers - no spam, only value.












